
“Feudalism” comes from the French féodalisme, a word coined during the French Revolution.Įvery peculiarity of policy, custom and even temperament is traced to this Feudal origin… I expect to see the use of trunk-hose and buttered ale ascribed to the influence of the feudal system (Humphry Clinker, 1771).įeudal society is a sometimes debated term used to describe the medieval social order of western and central Europe and sometimes Japan (particularly in the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries) characterized by the legal subjection of a large part of the peasantry to a hereditary landholding elite exercising administrative and judicial power on the basis of reciprocal private undertakings. Most of these laws and customs were related in some way to the medieval institution of the fief (Latin: Feodum, a word which first appears on a Frankish charter dated 884), and thus lumped together under this single term. It was a pejorative word used to describe any law or custom that was seen as unfair or out-dated. No writer in the period in which feudalism was supposed to have flourished ever used the word itself. The earliest known use of the term feudal was in the seventeenth century (1614), when the system it purported to describe was rapidly vanishing or gone entirely. Not until 1748 did it become a popular and widely used word, thanks to Montesquieu’s De L’Esprit des Lois (The Spirit of the Laws).

The word, “feudalism,” was not a medieval term, but an invention of sixteenth century French and English lawyers to describe certain traditional obligations between members of the warrior aristocracy. Roland pledges his fealty to Charlemagne from a manuscript of a chanson de geste / Wikimedia Commons As humankind progressed, however, this system was broken down and the Industrial Revolution changed the structure of societies, allowing greater development of science and technology in the modern age. As such, feudalism provided stability within societies, restoring public order and strengthening the monarchy.
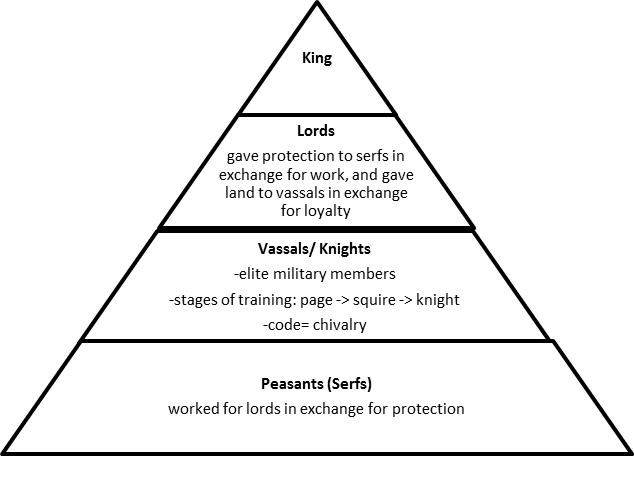
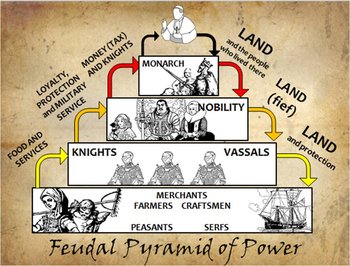
Generally, feudalism has been regarded as the fabric of medieval society, and the stage of social and economic development that preceded Capitalism. Outside of a European context, the concept of feudalism is normally only used by analogy (called “semi-feudal”), most often in discussions of Japan under the shoguns, and, sometimes, medieval and Gondarine Ethiopia. Since at least the 1960s, many medieval historians have included a broader social aspect, adding the peasantry bonds of manorialism, referred to as a “feudal society.” Still others, since the 1970s, have reexamined the evidence and concluded that feudalism is an unworkable term which should be removed entirely from scholarly and educational discussion, or at least only used with severe qualification and warning. However, other definitions of feudalism exist. This is a weak system and it refers to a general set of reciprocal legal and military obligations among the warrior nobility of Europe during the Middle Ages, revolving around the three key concepts of lords, vassals, and fiefs. Generally, feudalism has been regarded as the fabric of medieval society, and the stage of social and economic development that preceded Capitalism.įeudalism is a political system of power dispersed and balanced between king and nobles. Nuit du 4 août 1789 dans l’ Assemblée nationale française / Musée de la Révolution française, Wikimedia Commons


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
